Series: BPM (Business Process Management), Fundamentals, and Implementation Concepts – Do you know what a BPM is? What is it for? Do you need it in your company?
If something has been revealed in the business world, it is that globalization demands more and more organizations in their ability to react to changes. The ability to deal with them and adapt their offerings is part of the value they deliver to their customers.
Greater business agility and better efficiency must justify the value. Being efficient is no longer enough; a company must also be able to adapt to frequent changes (flexibility). For this, it is necessary to implement and maintain the company’s processes correctly: audits, tasks, creation of interfaces and forms, reports, etc.
This post focuses on business process management, its fundamentals, and implementation concepts.
Table of Contents
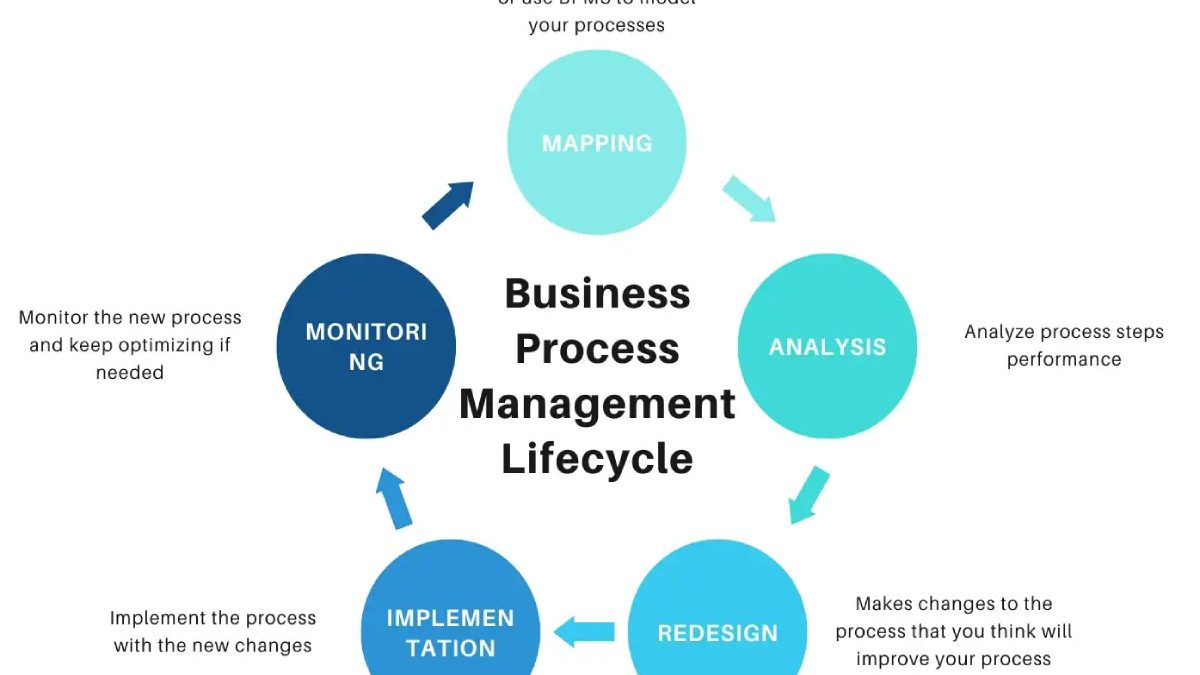
Definition Of BPM ( Business Process Management )
BPM is a work methodology oriented to process management that allows organizing and controlling the activities of a company’s employees. It implies following a series of steps or actions that modify how employees work to facilitate collaboration. Its ultimate goal is to improve company processes’ performance and optimization.

The main characteristics of a BPM system are:
- Business process modeling. It allows using a BPM to design end-to-end value chain processes regardless of the departments, tasks, or projects involved, both internal and from other organizations.
- Monitoring processes and users (KPIs) provides power and versatility by sharing information on operations and resource use status and detecting bottlenecks and inefficiencies in work teams.
- Data capture, management, and analysis. You must capture, manage, and analyze data related to the company’s processes, allowing you to feed analysis actions.
- Collaborative features. Functions can manage other employees’ absences, delegations, or assignments if the role and hierarchy are compatible.
- Easy document management. Process management generates a lot of documentary information associated with it and stores it in the BPM manager or external document systems.
- Some employees require the flexibility to make regular trips out of the office. Therefore, the BPM system should be available on mobile devices (smartphones and tablets).
- Generate a knowledge store. The memory of the actions carried out, who has intervened, what documents have been handled, or what decisions have been made become in the repository of the BPM system.
Now that you know the main features of Business Process Management or Business Process Management, it is time to delve into its fundamentals and evolution.
Fundamentals And Concepts Of BPM Implementation
The idea that business activities can be developed as a process is not new. At the beginning of the 20th century, Friedrick Winslow Taylor developed the concept of Scientific Management based on the standardization of processes in industrial production.
In the mid-90s, the well-known ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) appeared to solve companies’ management problems. However, these systems were not as efficient as expected, so improvements continued to be made. It was not until the late 1900s and early 2000s that CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems were developed to improve customer service.
Process engineering continues to evolve towards the current BPM, from Frederick Taylor’s first approach in 1911 to the overproduction of 1990 and the arrival of ERP and CRM. With the entry into the 21st century, companies began to pay more attention to business process management.
What Distinguishes These Systems From BPM
This is a straightforward idea. ERP and CRM fundamentally focus on data capture, while BPM focuses on process management. Let’s give an example to clarify this.
Suppose we have made a purchase. In the ERP, we would enter the supplier’s data, the product and model, the price of the acquisition, and the agreed way of paying it. On the contrary, the BPM would be in charge of managing the participants in the purchasing process: someone decides what is needed, another identifies the most qualified suppliers, another assesses the offers received, another confirms the purchase, and another manages the payment forecast.
Do they live parallel lives? In a way, yes. But with one crucial caveat: They share corporate data (budgets, suppliers, employees, etc.). According to the example described, the process would automatically enter that data in the ERP.
The Evolution Of Global Markets Requires Agile Methodologies
A company’s efficiency depends on proper process management. For this, management applications develop quickly and are adjusted and adjustable to each business’s specific needs.
Every company should prioritize saving time without compromising quality. Markets evolve, and evolution drives work with agile methodologies, which improve quality, satisfaction, engagement, and productivity.
What type of BPM does your company need? Are you one of those who believe in correct process management to achieve success?
Also Read:
This Blog Will Show You About The New Digital Technology In Thailand
Related posts
Featured Posts
Discover Different Types of Email Marketing and Its main KPIs
Types of Email Marketing – You have undoubtedly heard of email marketing recently. With the growth of digital transformation and…
What Risks can you Face in a Business IT Project
What Risks Can You Face in a Business IT Project? There are many risks associated with IT projects, as well…